Ground Water Quality Monitoring: Safeguarding a Vital Resource
Introduction
Groundwater is one of the most essential yet often overlooked resources on Earth. It sustains billions of people worldwide supporting drinking water, agriculture, and industry. But with increasing industrialization, population growth, and changing rainfall patterns, Ground water quality monitoring has become more important than ever.
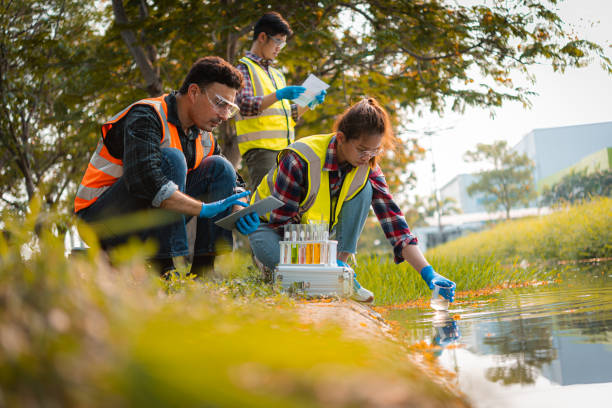
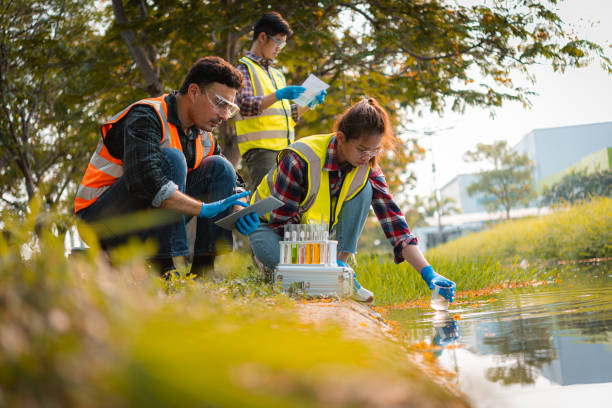
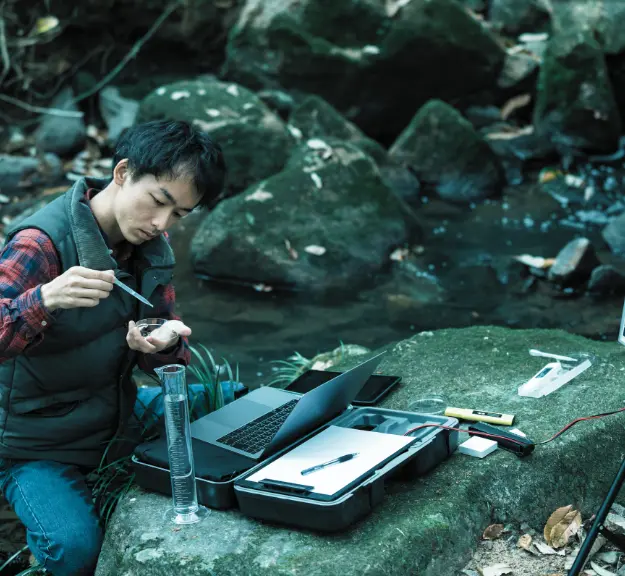
At The Ground Water Company (GWC), we specialize in scientific assessment, testing, and long-term monitoring of groundwater systems to ensure that communities, industries, and ecosystems have access to clean and safe water. By studying both surface and ground water quality, we help organizations and governments make informed decisions that protect public health and promote sustainable water management.
What Is Ground Water Quality Monitoring?
Ground water quality monitoring is the continuous process of assessing the physical, chemical, and biological properties of groundwater to determine whether it meets safety and environmental standards.
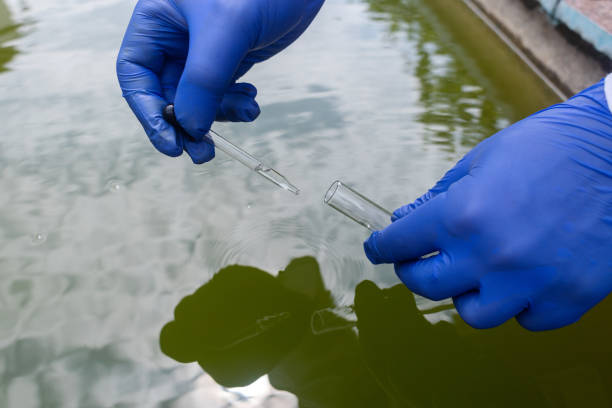
It involves collecting water samples from wells, boreholes, and aquifers at regular intervals and analyzing them for parameters like:
- pH, hardness, and alkalinity
- Nitrate, fluoride, and arsenic concentrations
- Heavy metals (lead, cadmium, chromium)
- Salinity and total dissolved solids (TDS)
- Bacterial contamination
Monitoring these indicators helps track pollution trends, identify contamination sources, and evaluate the factors affecting groundwater quality in specific regions.
Factors Affecting Groundwater Quality
Groundwater quality doesn’t deteriorate overnight it’s influenced by a combination of natural and human-made factors. Some key factors affecting groundwater quality include:
- Geological Composition
The minerals present in rocks and soils dissolve into groundwater as it flows through underground formations. For example, limestone areas often show higher hardness and calcium content. - Agricultural Activities
Excess use of fertilizers and pesticides leads to nitrate and chemical leaching, contaminating aquifers and nearby wells. - Industrial Discharges
Improper disposal of industrial waste and effluents introduces heavy metals and toxins into both surface and ground water quality systems. - Urbanization and Sewage Leaks
Leaking septic tanks, unlined landfills, and poor drainage networks cause bacterial contamination and chemical pollution. - Over-Extraction of Groundwater
Excessive pumping lowers water tables and alters the natural flow, allowing polluted surface water to seep downward.
Impact of Climate Change on Groundwater Quality
Climate change is not only altering rainfall patterns but also affecting the quality of groundwater. The impact of climate change on groundwater quality can be seen in several ways:
- Increased Salinity: Rising sea levels lead to saltwater intrusion in coastal aquifers, especially in states like Gujarat and Tamil Nadu.
- Reduced Recharge: Irregular and intense rainfall reduces natural groundwater recharge, concentrating pollutants in smaller water volumes.
- Temperature Rise: Higher temperatures accelerate chemical reactions and microbial growth, degrading water quality.
- Flooding & Drought: Floods cause contamination through sewage and runoff, while droughts lower water tables, pulling contaminants from deeper layers.
Without effective ground water quality monitoring, these subtle yet serious changes can go unnoticed until it’s too late.
Surface and Ground Water Quality: The Interconnection
Surface water (rivers, lakes, ponds) and groundwater are closely linked. Pollution in one system almost always impacts the other. For instance:
- Agricultural runoff entering rivers can infiltrate into aquifers.
- Industrial waste dumped into surface streams can percolate into groundwater through porous soil.
- Urban drainage containing chemicals and plastics seeps into shallow water tables.
Monitoring both surface and ground water quality ensures a complete picture of a region’s hydrological health and supports integrated water resource management.
Our Ground Water Quality Monitoring Services
At The Ground Water Company we provide end-to-end groundwater assessment and monitoring solutions, including:
- Baseline Quality Surveys – Initial analysis of aquifers for environmental compliance.
- Periodic Monitoring Programs – Seasonal sampling and testing for industries and municipalities.
- Real-Time Sensor Systems – IoT-based monitoring for continuous data collection.
- Hydrogeological Mapping – Identifying contamination sources and groundwater movement patterns.
- Remediation and Restoration Plans – Designing treatment systems to restore safe water conditions.
Our expert hydrogeologists and environmental engineers ensure data accuracy, regulatory compliance, and sustainable management for every project.
Benefits of Ground Water Quality Monitoring
- Protects Public Health: Ensures clean drinking water and reduces disease risk.
- Supports Sustainable Agriculture: Prevents crop loss from saline or contaminated irrigation water.
- Early Warning System: Detects contamination before it becomes widespread.
- Regulatory Compliance: Helps industries and municipalities meet pollution control norms.
- Informs Policy and Planning: Provides data for long-term water management and infrastructure design.
Conclusion
Groundwater is not an infinite resource and its quality defines the future of communities, agriculture, and industries alike. Continuous ground water quality monitoring is the first line of defense against pollution and degradation.
At The Ground Water Company (GWC), we combine hydrogeological expertise with modern testing and digital mapping to assess, monitor, and protect groundwater systems. By understanding the factors affecting groundwater quality and the impact of climate change on groundwater quality, we help ensure clean, reliable water for generations to come.