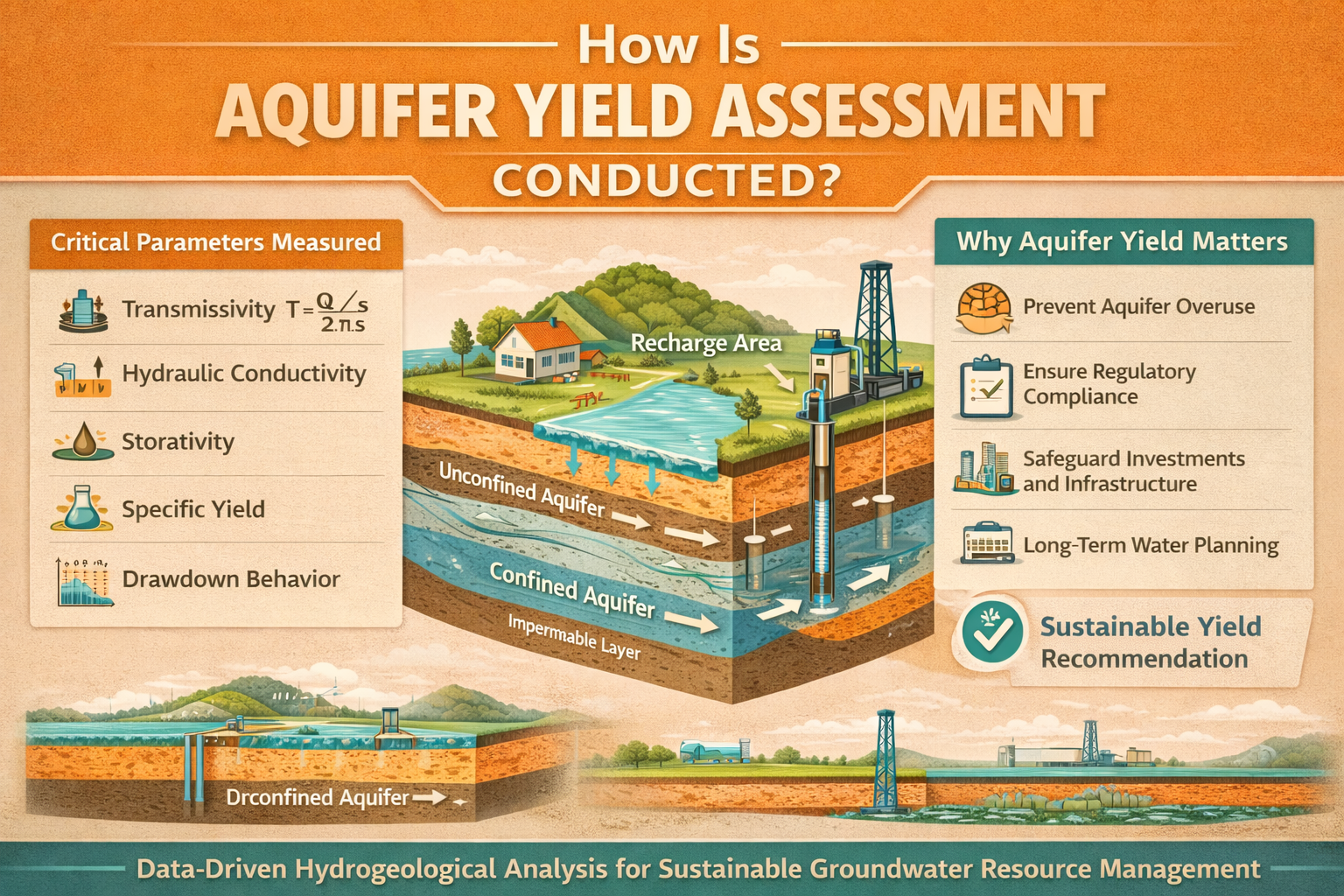
How Is Aquifer Yield Assessment Conducted?
Water beneath the surface may appear abundant, but aquifers have limits. Extracting groundwater without understanding its sustainable yield can result in rapid depletion, structural instability, regulatory violations, and long-term environmental damage.
Aquifer yield assessment is the scientific process used to determine how much groundwater an aquifer can sustainably produce without causing decline, subsidence, or ecological imbalance.
For real estate developments, it ensures reliable water supply and prevents structural risks.
For industries, it defines safe extraction limits.
For corporate and government projects, it supports regulatory approvals and long-term planning.
Understanding aquifer yield is not guesswork — it is data-driven hydrogeological analysis.
What Is Aquifer Yield?

Aquifer yield refers to the volume of water that can be extracted from an aquifer over time without:
Excessive drawdown
Long-term water table decline
Reduced recharge capacity
Inducing contamination migration
Causing land subsidence
It is different from simply drilling a borewell and observing water flow. Yield must be measured under controlled conditions using scientific testing.
Key Parameters Measured in Aquifer Yield Assessment
Aquifer yield assessment evaluates multiple hydrogeological variables:
Transmissivity
Hydraulic Conductivity
Storativity
Specific Yield
Recharge Rate
Drawdown Behavior
Recovery Rate
Each of these parameters determines the aquifer’s response to pumping stress.
The Step-by-Step Process of Aquifer Yield Assessment
1. Preliminary Hydrogeological Study
Before field testing begins, hydrogeologists evaluate:
Geological maps
Existing borewell data
Regional aquifer characteristics
Rainfall patterns
Recharge zones
Land use patterns
This establishes baseline expectations of aquifer behavior.
2. Exploratory Drilling and Borehole Logging

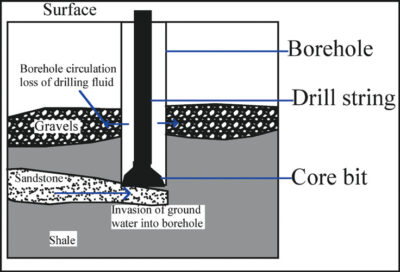
Drilling confirms:
Aquifer depth
Lithology
Fracture systems
Water-bearing strata
Thickness of aquifer layers
Borehole logging records subsurface geological formations and water entry points.
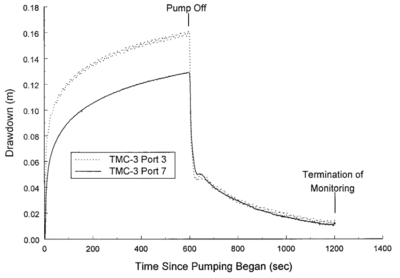
3. Pumping Test (Core Stage)
The pumping test is the primary method used in aquifer yield assessment.
During this test:
Water is pumped at a constant discharge rate
Water level decline (drawdown) is recorded at regular intervals
Observation wells measure impact radius
Recovery is monitored after pumping stops
This test provides real-time aquifer response data.
Detailed aquifer behavior and pumping test interpretation methods are extensively documented in the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) groundwater science resources.
4. Drawdown Curve Analysis
The relationship between time and water level decline is plotted as a drawdown curve.
This helps determine:
Aquifer transmissivity
Storage coefficient
Sustainable discharge rate
Radius of influence
Sustainable discharge rates are calculated using standardized approaches similar to those described in USGS aquifer test methodology.
Mathematical models such as the Theis equation or Cooper-Jacob method are often applied to interpret pumping test results.
5. Calculation of Transmissivity and Storativity
Transmissivity measures how easily water moves through the aquifer.
Storativity measures the volume of water released per unit decline in hydraulic head.
These calculations determine:
Maximum sustainable pumping rate
Long-term aquifer behavior
Extraction safety limits
6. Long-Term Yield Estimation
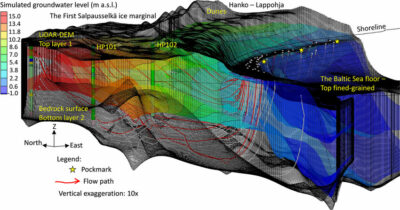
Short pumping tests show immediate response, but sustainable yield must consider:
Recharge rates
Seasonal fluctuations
Climate variability
Future demand growth
Nearby extraction impacts
Groundwater modelling may be used to simulate long-term scenarios.
Infographic Section (Recommended Visual)
Title: Aquifer Yield Assessment Workflow
Flow:
Preliminary Study → Drilling → Pumping Test → Drawdown Analysis → Transmissivity Calculation → Long-Term Modelling → Sustainable Yield Recommendation
This visual reinforces technical credibility.
Why Aquifer Yield Assessment Is Critical for Real Estate
High-rise developments with basements are vulnerable to:
Water table fluctuation
Hydrostatic uplift
Foundation seepage
Excavation instability
If extraction is too aggressive, surrounding groundwater pressure changes can affect structural stability.
Yield assessment ensures controlled extraction aligned with site safety.
Why Industries Must Conduct Yield Assessment
Industries relying on groundwater for operations risk:
Production shutdown
Regulatory penalties
Increased operational cost
Aquifer depletion
Yield assessment defines:
Daily allowable extraction
Emergency reserve capacity
Recharge requirements
It protects both business continuity and environmental sustainability.
Regulatory and Compliance Importance
Many jurisdictions require:
Aquifer yield reports
Pumping test documentation
Groundwater extraction permits
Environmental clearance reports
Yield assessment forms a core component of hydrogeological investigation reports required for compliance.
Common Mistakes Without Proper Yield Assessment
Drilling without testing
Overestimating borewell discharge
Ignoring seasonal variation
Not monitoring recovery rate
Failure to assess neighboring extraction impact
These mistakes lead to declining water tables and long-term risk.
Difference Between Instant Borewell Yield and Sustainable Yield
Instant Yield:
Short-term discharge rate observed immediately after drilling.
Sustainable Yield:
Scientifically determined long-term extraction capacity without aquifer stress.
The two are not the same — and confusing them leads to aquifer depletion.
Advanced Techniques Used in Yield Assessment
Step-drawdown testing
Constant-rate pumping test
Observation well monitoring
Geophysical correlation
Groundwater numerical modelling
These techniques improve accuracy and reduce risk.
How Aquifer Yield Assessment Supports Climate Resilience
Climate change alters:
Recharge cycles
Rainfall intensity
Drought duration
Aquifer recharge rates
Yield assessment integrates climate data to ensure long-term sustainability.
When Should Aquifer Yield Assessment Be Conducted?
Before land acquisition
Before borewell drilling
Before industrial setup
Before large-scale water extraction
Before infrastructure development
Early assessment reduces project risk significantly.
How This Connects to Hydrogeological Investigation
Aquifer yield assessment is a core component of a complete hydrogeological investigation.
While the broader investigation studies aquifer behavior, contamination risk, and recharge systems, yield assessment specifically quantifies extraction capacity.
Together, they provide a full groundwater feasibility framework.
Conclusion
Aquifer yield assessment is not simply a technical formality. It is a scientific safeguard that protects infrastructure, industry, and public water resources.
Through pumping tests, drawdown analysis, transmissivity calculation, and groundwater modelling, hydrogeologists determine how much water an aquifer can sustainably supply.
Projects that invest in accurate yield assessment build responsibly and operate sustainably.
Call to Action
If your real estate, industrial, or infrastructure project depends on groundwater extraction, a professional aquifer yield assessment should be your first step.
Consult experienced groundwater specialists before committing to extraction strategies.
Visit our Groundwater Consulting page to learn more about professional hydrogeological investigation services.