What Is a Hydrogeological Investigation and Why Is It Required?
Water beneath the ground is invisible — but it directly determines the feasibility, safety, compliance, and sustainability of infrastructure projects. Whether it is a high-rise development, industrial manufacturing unit, mining project, corporate campus, or government infrastructure expansion, understanding subsurface water conditions is not optional.
It is fundamental. A hydrogeological investigation is a scientific assessment of groundwater conditions within a specific geographic area. It evaluates aquifer characteristics, groundwater flow systems, recharge potential, yield capacity, contamination risk, and regulatory viability before groundwater extraction or development begins.
For real estate developers, it prevents basement uplift, seepage, and foundation instability. For industries, it ensures sustainable water extraction and regulatory compliance. For corporate entities, it reduces operational water risk.
For government bodies, it supports long-term water security and policy planning. Without a structured hydrogeological investigation, projects move forward blindly — often resulting in cost overruns, environmental violations, structural issues, and water scarcity challenges.
What Exactly Does a Hydrogeological Investigation Study?
At its core, hydrogeology is the study of groundwater — its occurrence, movement, quality, and interaction with geological formations.
As defined by the International Association of Hydrogeologists (IAH), hydrogeology integrates geology, hydrology, and environmental science to evaluate subsurface water systems and their sustainable management.
A professional hydrogeological investigation typically examines:
Aquifer type and depth
Hydraulic conductivity and transmissivity
Storativity and yield potential
Groundwater table fluctuation
Recharge and discharge mechanisms
Subsurface lithology and fracture systems
Groundwater contamination risks
Surface-groundwater interaction
Regulatory extraction limits
It combines geology, hydrology, geophysics, environmental science, and engineering analysis.
Why Is Hydrogeological Investigation Required Before Development?
1. Structural Stability in Real Estate Projects
Improper understanding of groundwater pressure can lead to:
Basement uplift
Retaining wall failure
Persistent seepage
Soil liquefaction risks
Foundation weakening
Hydrostatic pressure from a high groundwater table can exert significant uplift force on underground structures. Without prior assessment, costly retrofitting becomes inevitable.
2. Sustainable Water Extraction for Industries
Industrial facilities often rely heavily on groundwater for:
Process water
Cooling systems
Manufacturing operations
Sanitation and domestic use
A hydrogeological investigation determines:
Safe extraction limits
Aquifer recharge capacity
Long-term sustainability
Risk of over-extraction
Over-pumping without assessment leads to aquifer depletion, land subsidence, and regulatory action.
3. Compliance and Regulatory Approval
Many jurisdictions globally require:
Aquifer yield assessment
Groundwater modelling
Pumping test reports
Impact assessment studies
Hydrogeological investigations provide scientific documentation required for groundwater extraction permissions.
Regulatory frameworks governing groundwater extraction and drinking water safety are often aligned with environmental protection standards established by agencies such as the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), which provides guidance on groundwater protection and sustainable resource management.
4. Risk Management for Corporate and Government Projects
Water risk is now an ESG and sustainability issue. Corporations and public institutions must evaluate:
Climate resilience
Drought vulnerability
Flood interaction
Groundwater contamination pathways
A hydrogeological investigation forms the backbone of water risk assessment frameworks.
The Scientific Process of Hydrogeological Investigation
Below is the structured flow followed in professional groundwater consulting projects.
Step 1: Desk Study and Data Collection
This includes:
Satellite imagery review
Geological maps
Historical borewell records
Hydrological data
Rainfall patterns
Land use patterns
This stage identifies aquifer types and possible groundwater zones.
Step 2: Field Reconnaissance
On-site investigation evaluates:
Surface drainage conditions
Topography
Soil profile
Existing wells
Seepage patterns
Field data validates preliminary findings.
Step 3: Geophysical Survey
Common techniques include:
Electrical Resistivity Survey
Seismic Refraction
Electromagnetic Surveys
These methods help detect:
Aquifer thickness
Fracture zones
Water-bearing formations
Subsurface layering
Step 4: Exploratory Drilling and Borehole Logging
Core sampling and borehole logging provide:
Lithological profile
Fracture mapping
Water-bearing strata identification
Depth of bedrock
This stage confirms aquifer structure.
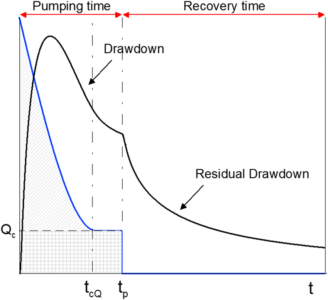
Step 5: Pumping Test Analysis
Pumping tests evaluate:
Aquifer yield
Drawdown behavior
Transmissivity
Storativity
Recovery rates
This determines sustainable extraction capacity.
Step 6: Groundwater Modelling
Mathematical models simulate:
Long-term extraction impact
Recharge potential
Future water table behavior
Contaminant migration risk
Groundwater modelling ensures development does not cause future instability.
Step 7: Technical Reporting and Recommendations
Final deliverables include:
Hydrogeological report
Aquifer capacity assessment
Extraction guidelines
Recharge recommendations
Risk mitigation strategy
These form the foundation of project decision-making.
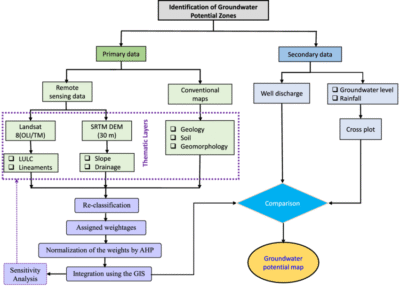
Infographic Structure For Blog Visual Understanding
Title: Hydrogeological Investigation Workflow
Flow:
Desk Study → Field Survey → Geophysical Investigation → Drilling & Logging → Pumping Test → Groundwater Modelling → Technical Report → Sustainable Extraction Plan
This can be visually structured as a horizontal technical process diagram.
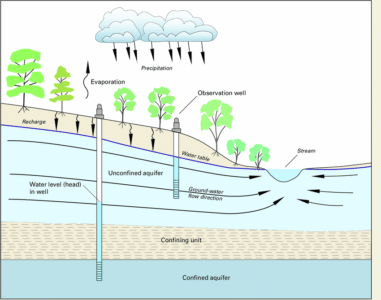
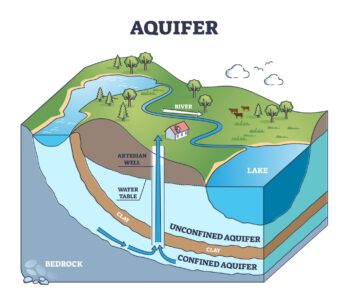
Technical Diagram Explanation Section
Diagram Concept:
Cross-sectional aquifer diagram showing:
Surface layer
Unsaturated zone
Water table
Confined aquifer
Unconfined aquifer
Recharge zone
Extraction well
Flow direction arrows
Explanation:
The diagram illustrates how groundwater flows through permeable layers and how extraction impacts surrounding hydraulic gradients.
Key Technical Parameters Evaluated
Hydraulic Conductivity
Transmissivity
Storativity
Specific Yield
Recharge Rate
Groundwater Gradient
Drawdown Curve
Recovery Curve
Each parameter determines extraction viability and structural safety.
How Hydrogeological Investigation Reduces Project Risk
For Real Estate Developers:
Prevents basement uplift
Controls seepage
Ensures stable foundation design
For Industries:
Prevents water scarcity
Ensures compliance
Reduces operational risk
For Government Bodies:
Supports infrastructure planning
Protects public water resources
Prevents aquifer depletion
Global Importance in a Climate-Resilient World
Climate change has intensified:
Extreme rainfall events
Drought cycles
Groundwater stress
Urban flooding
Hydrogeological investigation is no longer optional — it is a climate adaptation strategy.
Understanding aquifer behavior under changing climatic conditions ensures long-term resilience.
When Should You Conduct a Hydrogeological Investigation?
Before land acquisition
Before drilling borewells
Before basement excavation
Before industrial water dependency planning
Before regulatory approvals
Before large infrastructure investments
Early-stage investigation reduces long-term cost and liability.
Common Mistakes Without Proper Investigation
Drilling without yield assessment
Ignoring aquifer recharge limits
Underestimating hydrostatic pressure
Over-extracting groundwater
Failing compliance documentation
These errors can delay projects and cause structural damage.
How The Ground Water Company Supports Hydrogeological Investigations
The Ground Water Company provides structured groundwater consulting services globally for:
Real estate developers
Industrial corporations
Corporate campuses
Government infrastructure projects
Our approach integrates:
Scientific field methods
Advanced geophysical surveys
Pumping test analysis
Groundwater modelling
Risk-based extraction planning
Learn more about our professional consulting services here:
https://thegroundwatercompany.com/ground-water-consulting/
Conclusion
A hydrogeological investigation is not just a groundwater study. It is a scientific risk assessment that protects infrastructure, ensures regulatory compliance, and safeguards long-term water sustainability.
Projects that invest in proper hydrogeological evaluation build safely, operate sustainably, and avoid costly failures.
For organizations planning new developments or evaluating water dependency risks, scientific groundwater assessment should be the first step — not the last.
CALL TO ACTION
If your project depends on groundwater stability, extraction, or compliance, consult experts before making critical decisions.
Visit our Contact Page to discuss your hydrogeological investigation requirements with our technical team.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Hydrogeological investigation is the scientific study of groundwater conditions including aquifer characteristics, flow systems, recharge potential, and sustainable extraction capacity.
It prevents structural damage, basement uplift, seepage issues, and ensures sustainable water extraction.
Geophysical surveys, drilling, borehole logging, pumping tests, groundwater modelling, and laboratory analysis.
Real estate developers, industrial facilities, corporate campuses, mining companies, and government bodies.
Duration depends on project scale, site conditions, and required testing but typically ranges from several weeks to a few months.












One thought on “What Is a Hydrogeological Investigation and Why Is It Required?”