Ground Water Recharge: Sustaining Aquifers for the Future
Introduction
Ground Water Recharge is one of the most vital components of sustainable water management. As urbanization, population growth, and industrial activity continue to strain existing freshwater sources, the need to replenish underground aquifers has never been more urgent. At The Ground Water Company (GWC), we focus on scientifically driven recharge solutions that combine modern innovation with natural processes to restore groundwater balance and ensure long-term water security.
Groundwater Recharge
Groundwater recharge methods refer to the natural or artificial processes through which surface water seeps into the ground and replenishes aquifers. This process maintains the natural hydrological cycle, sustains wells and springs, and supports agriculture, ecosystems, and human settlements.
While natural groundwater recharge occurs through rainfall infiltration, river seepage, and percolation through soil layers, urbanization has severely reduced these pathways. Concrete surfaces, deforestation, and poor water management limit infiltration, leading to declining groundwater levels. This is where engineered or artificial groundwater recharge methods become essential.
Artificial Groundwater Recharge Techniques
To supplement natural infiltration, engineers use various artificial groundwater recharge techniques that accelerate the process of percolation and storage. At GWC, our designs are tailored to local geological, hydrological, and climatic conditions. Common approaches include:
- Recharge and Shafts
Shallow pits or vertical shafts that allow rainwater to percolate directly into aquifers beneath residential and industrial areas. - Percolation Tanks
Small reservoirs that collect rainwater runoff, allowing gradual seepage into the ground. - Recharge Wells
Deep structures that channel clean rainwater directly into depleted aquifers through filtered systems. - Check Dams and Contour Bunds
Small barriers constructed across streams or slopes to slow down water flow and promote infiltration. - Recharge Trenches and Injection Wells
Linear structures that collect stormwater and direct it into permeable soil or fractured rock formations for deep aquifer recharge.
Each method demonstrates how groundwater recharging can be achieved by merging scientific precision with nature’s own filtration and storage mechanisms.
Groundwater Recharge and Rain
The relationship between groundwater recharge and rain is fundamental. Rainwater acts as the primary source for replenishing aquifers, but without proper systems to capture and direct it, much of this precious resource is lost as surface runoff. Integrating rain water harvesting and ground water recharge systems allows cities and villages alike to convert seasonal rainfall into year-round supply.
At GWC, we implement customized solutions such as rooftop collection systems, infiltration trenches, and decentralized recharge pits that ensure every drop of rain contributes to aquifer replenishment.
Underground Water Recharge: The Hidden Reservoir
Underground water recharge is the silent foundation of sustainable water supply. When water seeps through soil and rock layers, it not only refills aquifers but also undergoes natural filtration, improving water quality. By enhancing infiltration zones through green infrastructure and land management, communities can strengthen groundwater resilience even during dry seasons.
Managing Aquifer Recharge: A Showcase for Resilience and Sustainability
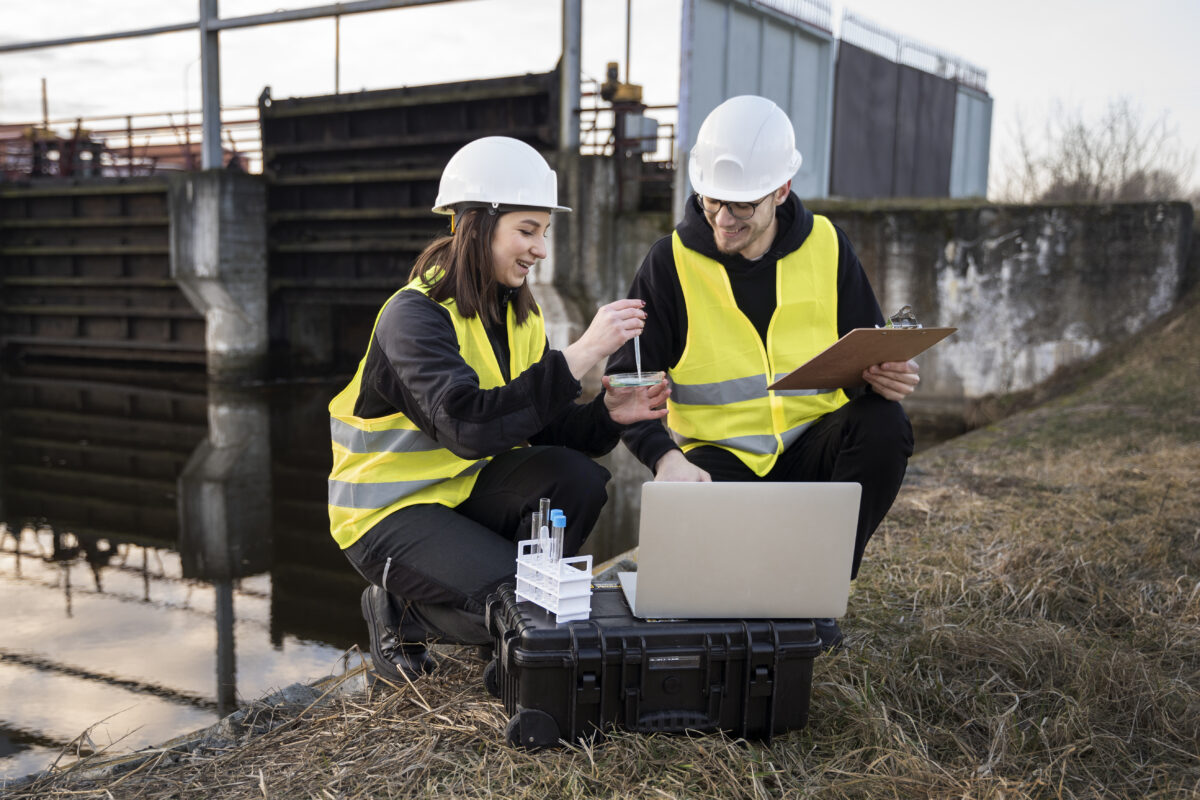
Modern water conservation demands a proactive approach to managing aquifer recharge a showcase for resilience and sustainability. Effective management includes identifying recharge zones, preventing over-extraction, and monitoring aquifer health using advanced tools like GIS mapping, piezometers, and remote sensing.
At The Ground Water Company, our integrated recharge management systems combine hydrogeological studies with long-term sustainability goals, ensuring that aquifers remain productive and healthy for generations.
Benefits of Ground Water Recharge
- Restores Depleted Aquifers: Replenishes groundwater tables in drought-prone and over-exploited regions.
- Reduces Flooding and Runoff: Captures excess rainwater, minimizing urban flooding and soil erosion.
- Improves Water Quality: Natural percolation filters out contaminants and enhances groundwater purity.
- Supports Agriculture and Industry: Ensures reliable water for irrigation, manufacturing, and domestic use.
- Promotes Climate Resilience: Helps communities adapt to changing rainfall patterns and prolonged droughts.
The Ground Water Company’s Approach
At GWC, we develop data-driven groundwater recharge systems customized to regional geology and water demand. From designing artificial groundwater recharge methods for industrial estates to implementing community-based rainwater harvesting programs, our solutions promote long-term aquifer sustainability.
Our expertise extends across:
- Hydrogeological mapping and site assessment
- Design and construction of recharge structures
- Water quality analysis and monitoring
- Integration of IoT-based monitoring and maintenance
Conclusion
Ground Water Recharge is more than a technical process it is a commitment to balance, sustainability, and survival. By combining natural groundwater recharge with modern artificial groundwater recharge techniques, we can restore aquifers, reduce dependency on external water sources, and ensure lasting water security.
At The Ground Water Company (GWC), we bring together science, engineering, and environmental stewardship to transform the way water is managed below the surface. Our goal is clear: to secure the planet’s underground reserves, protect communities, and make groundwater management a model of resilience and sustainability.